What sets plasma spraying apart from HVOF thermal spray coatings?
In thermal spraying, these two methods stand out as the primary processes. While both involve heating material to high temperatures and projecting it onto a surface, nuances distinguish them.
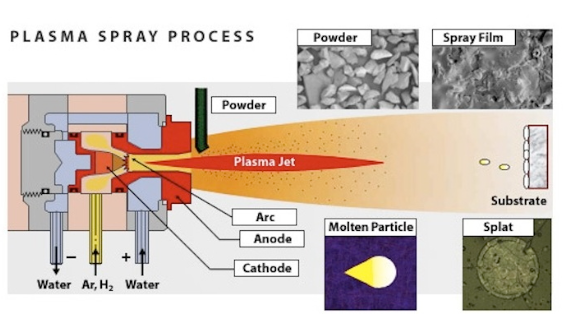
Plasma spraying employs a plasma torch in order to heat the material, creating a plasma plume of very high temperature. Material heated and propelled within this plume is directed at the surface where it solidifies into a coating.
Conversely, HVOF relies on the combustion of a fuel gas like hydrogen or propane to heat the material. This generates an exceedingly fast jet of gas, accelerating the material towards the surface.
The pivotal difference lies in the velocity of the material being sprayed. Plasma deposits tend to be sprayed at lower velocities than HVOF-sprayed materials, resulting in a lower-density coating.
What advantages do plasma coatings offer?
Plasma spray coatings exhibit higher density than traditional flame spray coatings using wire or powder. Also, the process can achieve significantly elevated temperatures, enabling the application of materials with very high melting points.
In addition, plasma spray guns are compact and lightweight, with a short standoff distance. This allows plasma spraying to be conducted in confined spaces, such as tubular IDs, more effectively than other thermal spray methods.
For those interested in learning more about plasma spraying, contacting a specialist such as www.poeton.co.uk/standard-treatments/plasma-coatings could provide valuable insights.

Which materials are frequently used in plasma spraying processes?
The materials employed in plasma spraying encompass metals, ceramics, and composites. Metals, including aluminium, chromium, and nickel, are favoured for their exceptional wear and corrosion resistance. Ceramics such as alumina and zirconia are sought after for their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist wear. Additionally, composites like tungsten carbide are valued for their superior wear resistance.
